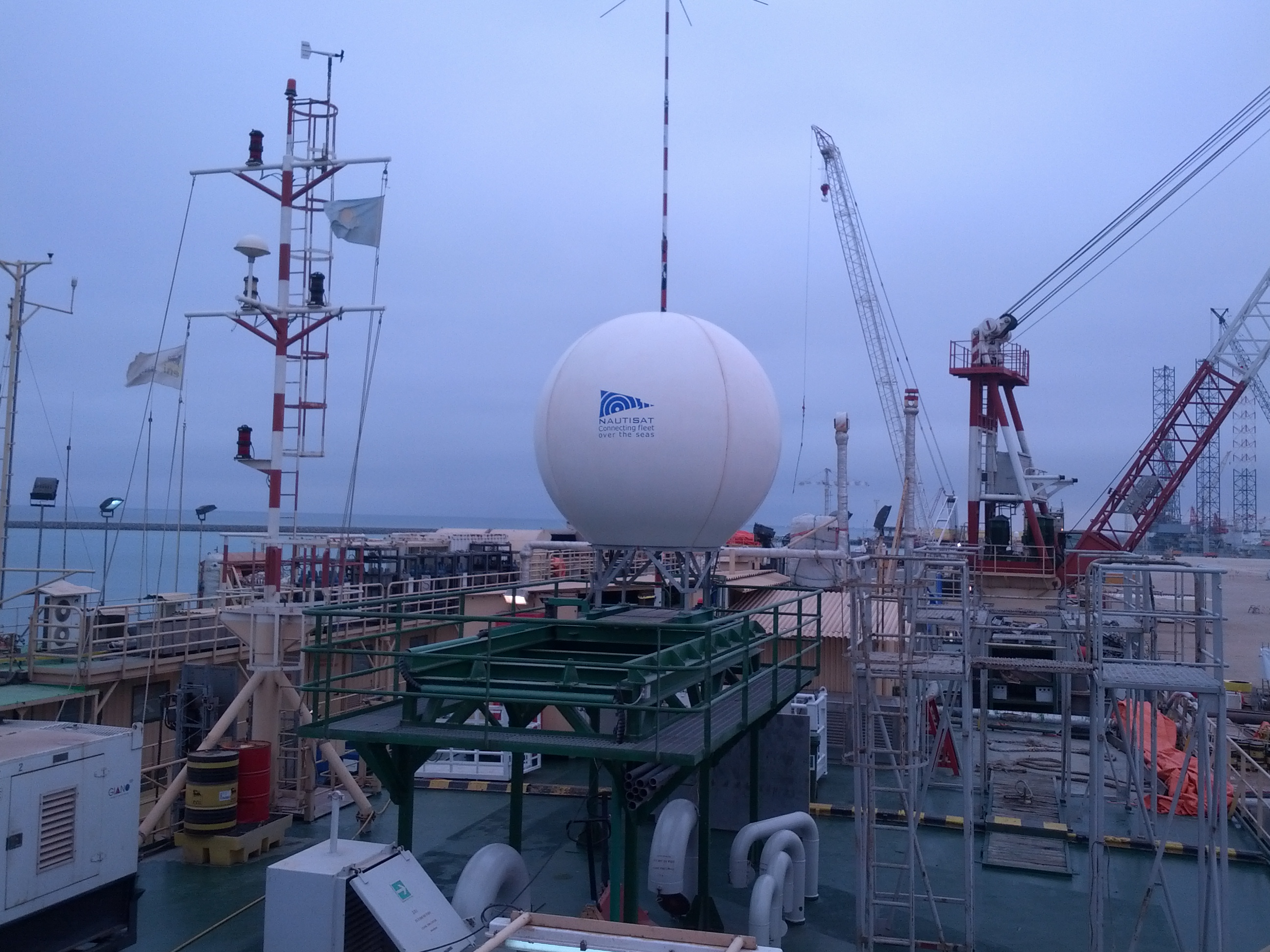
Nautisat
Discover NAUTISAT: Your Premier Provider of TVRO and VSAT Maritime Antennas Since 2001
For over two decades, NAUTISAT has been at the forefront of delivering top-of-the-line TVRO and VSAT maritime antennas, renowned for their simplicity, durability, and unrivaled functionality. Our antennas require no assistance, ensuring seamless operation even in the most challenging maritime environments.
About NAUTISAT
NAUTISAT is a trailblazing company dedicated to providing state-of-the-art technological solutions tailored to the unique communication needs of the maritime industry. With a relentless commitment to customer satisfaction, we offer an extensive array of engineering and technological solutions.
Our Comprehensive Services
From the meticulous design to the seamless installation of cutting-edge satellite communication systems, NAUTISAT provides end-to-end solutions. Our services encompass dedicated technical support, regular maintenance, and comprehensive personnel training, ensuring optimal performance and peace of mind for our valued clients.
Why Choose NAUTISAT?
What sets NAUTISAT apart is our unwavering dedication to excellence and surpassing customer expectations. With a seasoned team boasting extensive industry experience, we guarantee unparalleled service quality and reliability.
Empowering Your Journey
Whether you're seeking dependable communication solutions at sea or customized design strategies for unique challenges, NAUTISAT has you covered. Count on us to navigate you with confidence through every stage of your journey. Simplicity and Effectiveness Redefined
Simplicity and Effectiveness Redefined
At NAUTISAT, we prioritize simplicity and effectiveness. Our products feature user-friendly interfaces and deliver exceptional performance with minimal maintenance requirements. We're committed to staying ahead of technological advancements to provide you with the most efficient and reliable solutions available.
Experience NAUTISAT Excellence Today
Experience the NAUTISAT difference today and elevate your maritime communication experience to new heights. Trust NAUTISAT for unmatched quality, reliability, and innovation.
Our Products and Services
We offer a range of solutions to ensure your experience at sea is safe, efficient and enjoyable.
But not only that, we offer technical and engineering consultancy to create the best solutions for your specific needs.
With our experience and knowledge, we can help you find the best options for your project to be implemented with innovative, solid and effective solutions.

VSAT and TVRO
Sailing the open ocean is an exhilarating adventure, yet it also comes with its challenges and risks. That's where our expertise and technology come into play, helping to mitigate these risks and ensure safe and enjoyable browsing experiences.
Whether you're navigating remote waters or cruising along the coastline, our solutions are designed to enhance your maritime experience and keep you connected wherever you go. Trust NAUTISAT to be your partner in seamless communication and entertainment at sea.
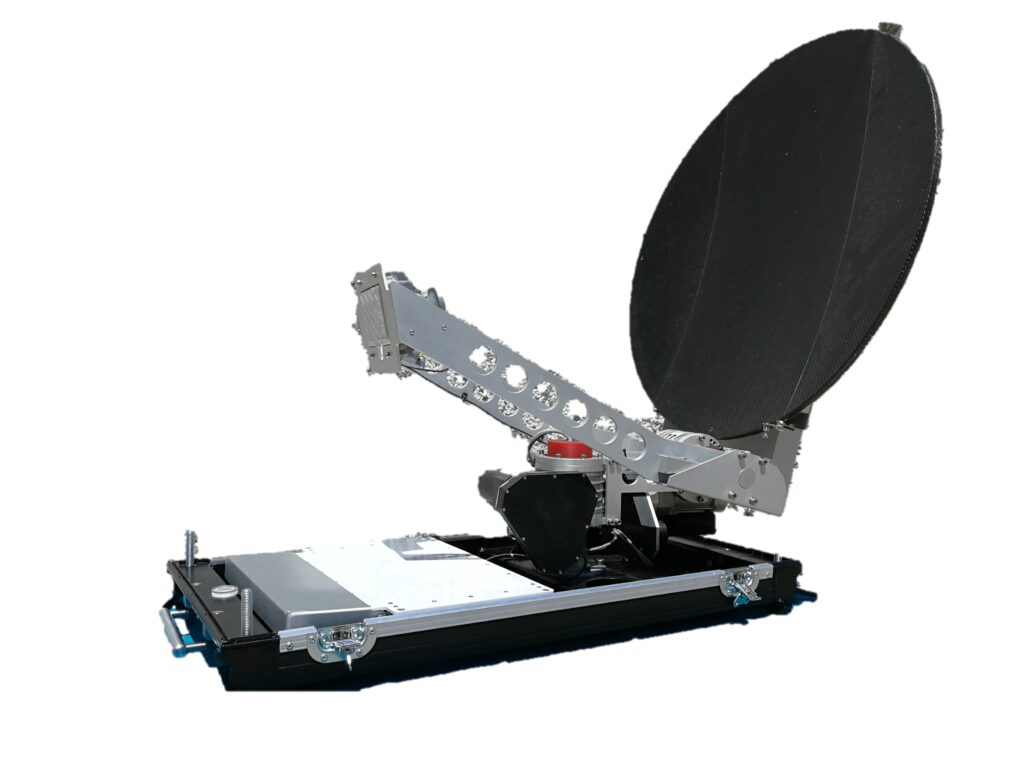

Nautifly
This innovative solution offers unmatched convenience for maritime communication needs, allowing for easy transportation and quick deployment. With its compact design and reliable performance, the NAUTIFLY 75 ensures seamless connectivity even in remote maritime environments.
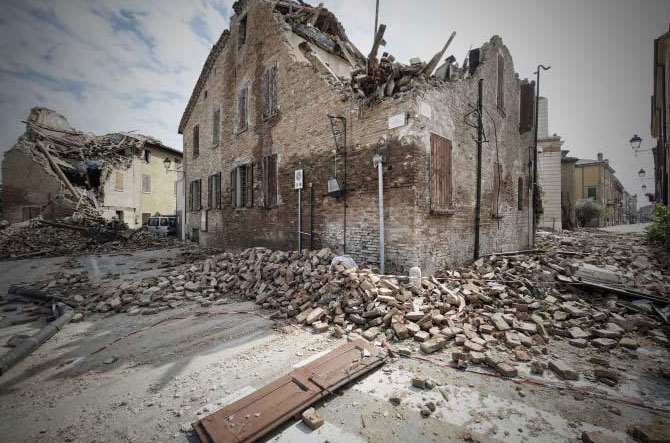

Disaster Recovery
NAUTISAT provides reliable satellite communication solutions that remain operational even in the face of such emergencies. Our advanced technology ensures uninterrupted connectivity, facilitating timely communication and aiding rescue operations in critical situations.
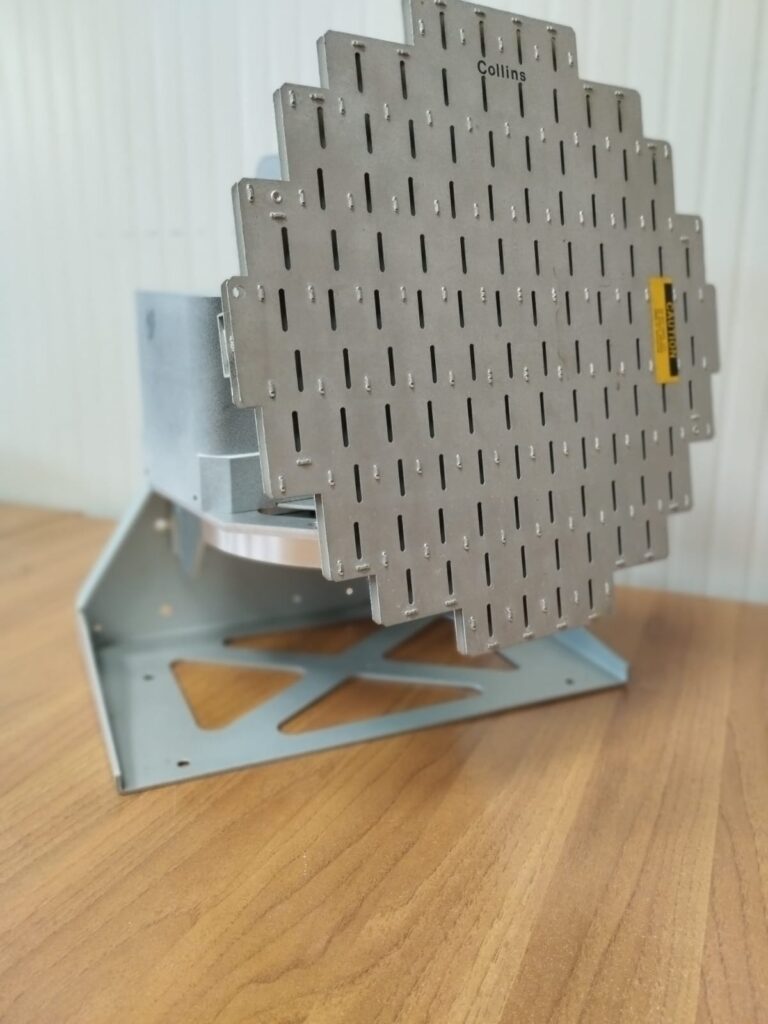

Meteo Radar for Airplane
The primary challenge was to develop a compact yet high-performance product capable of operating effectively in extreme conditions.
NAUTISAT met this challenge head-on, delivering a cutting-edge solution that ensures optimal performance even in the most demanding environments.

Nautiland
Connection on the go
This innovative system offers unparalleled connectivity and mobility, making it ideal for a wide range of applications in remote or rugged environments. Whether you're in the field, on the road, or off-grid, Nautiland 120 ensures reliable communication and data access wherever your adventures take you.
Trust Nautiland 120 to deliver superior performance and flexibility for all your communication needs.

CoSAT
SPECIAL PROJECTS AND FUNDED RESEARCH CALL
This is achieved with the co-siting technologies made available by ROMA TRE. The great development of satellite applications for IOT and M 2 M has seen the need to use antennas. In the uhf band usable by cubesat. But to realize significant gains, antennas need to be large and compressible at launch and then deployed in flight.
This is achieved by NAUTISAT by designing a flight-deployable helix antenna.
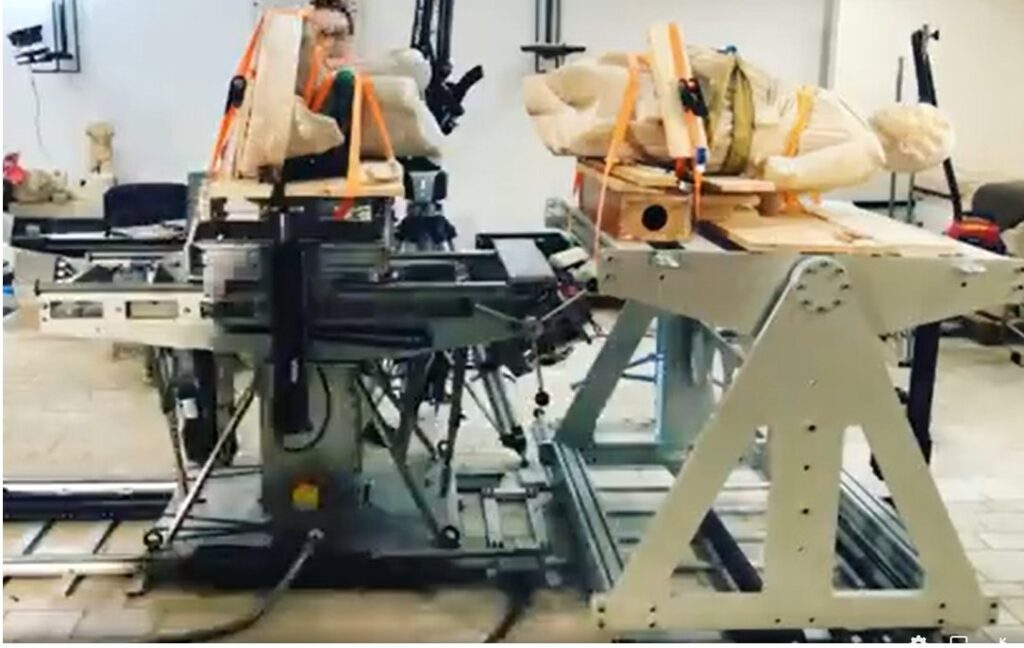
MACORè
ART PROJECT DEVELOPMENT
Our innovative solution streamlines and simplifies the intricate phases of stone restoration, contributing to the preservation of cultural heritage and ensuring the longevity of historical structures. With the ReStart system, restoration professionals can achieve superior results with efficiency and precision, ushering in a new era of conservation excellence.

ATC CONTROL RADARS
Our proprietary software is utilized to meticulously design the profile reflector and feed/polarizer system, ensuring optimal performance and precision. The innovative off-set profile of the reflector minimizes side lobes to an unprecedented level, enhancing the radar's accuracy and reliability.
Experience the pinnacle of radar technology with the Nautisat S-Band A.T.C. antenna system, designed to meet the demands of the most discerning users.
Why Choose Us
FLEXIBILITY
Customer satisfaction is our top priority. We prioritize the needs of our customers, ensuring that their requests are met promptly and precisely. By placing the customer at the center of our activities, we are committed to delivering tailored solutions that align with their specific requirements, providing a seamless and responsive experience every step of the way.
PROFESSIONALISM
We pride ourselves on our team of experienced and highly qualified professionals who consistently deliver high-quality services to our valued customers. With a strong emphasis on ethical integrity, we uphold rigorous standards of reliability in all our endeavors. We are dedicated to meeting deadlines and honoring commitments made to our customers, thereby fostering trust and credibility at every interaction. Our unwavering commitment to maintaining a high level of trust and credibility ensures that our customers can rely on us for exceptional service and support.
QUICKNESS
We prioritize timeliness in addressing customer requests, ensuring swift and effective solutions to meet their needs. We are dedicated to optimizing resources and reducing costs wherever possible, without compromising on quality or reliability. By streamlining our processes and leveraging innovative techniques, we strive to deliver efficient and cost-effective solutions that exceed customer expectations.
EXCELLENCE
Our commitment to excellence drives us to deliver the highest quality services to our customers. We utilize top-tier materials, cutting-edge technologies, and advanced production processes to ensure superior results. Our dedication to innovation allows us to provide creative and innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of our clients. With Nautisat, you can trust that you're receiving the best-in-class service and solutions for your maritime communication needs.
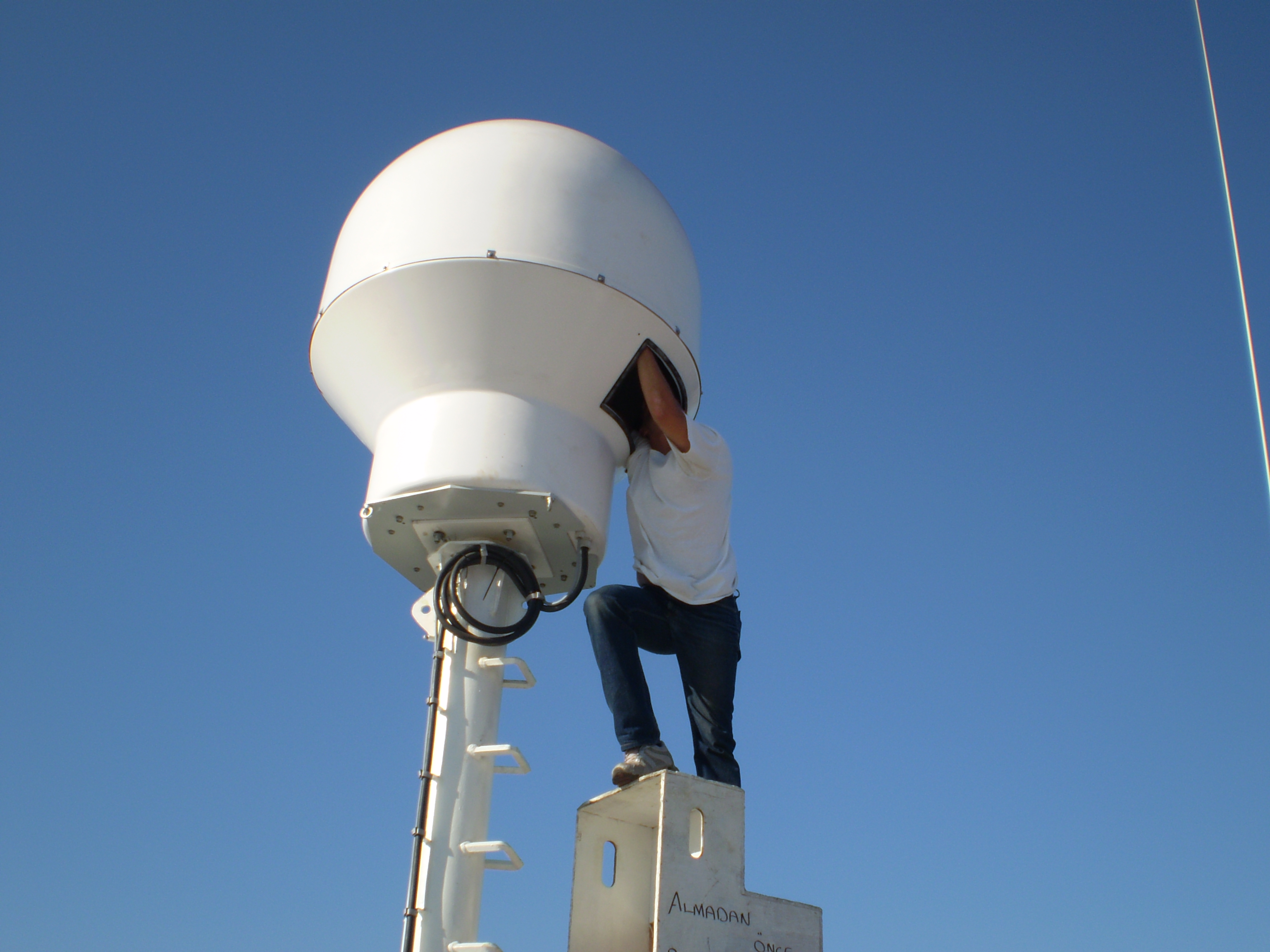

About Our
Company
Nautisat stands as a premier designer, manufacturer, and installer of VSAT satellite communications antennas and TVRO systems, catering to a diverse clientele including commercial vessels, oil platforms, and yachts of all sizes. With a legacy dating back to 2001, our dedicated team of expert designers and skilled workers collaborates seamlessly to deliver high-grade products, ranging from large 300cm dish antennas to more compact 60cm models.
Each Nautisat Antenna System undergoes meticulous design and development within our state-of-the-art laboratories. Our commitment to innovation ensures that every system, both in its mechanical and electrical components, evolves into a well-engineered and cost-balanced product, meeting the highest standards of performance and reliability in maritime communication solutions.
Nautisat services are a winning choice thanks to the wide range of customizable services, reliable technical support, product quality, company experience and its reputation for reliability and customer satisfaction.
